Have you ever wondered about the differences between Pediatric Physiotherapy (PT) and Pediatric Occupational Therapy (OT)? While these two disciplines share similarities, they also have distinct roles in helping individuals, including children, improve their quality of life. Both require specialized training and are regulated by provincial colleges to ensure the highest standards of care.
What is Physiotherapy?
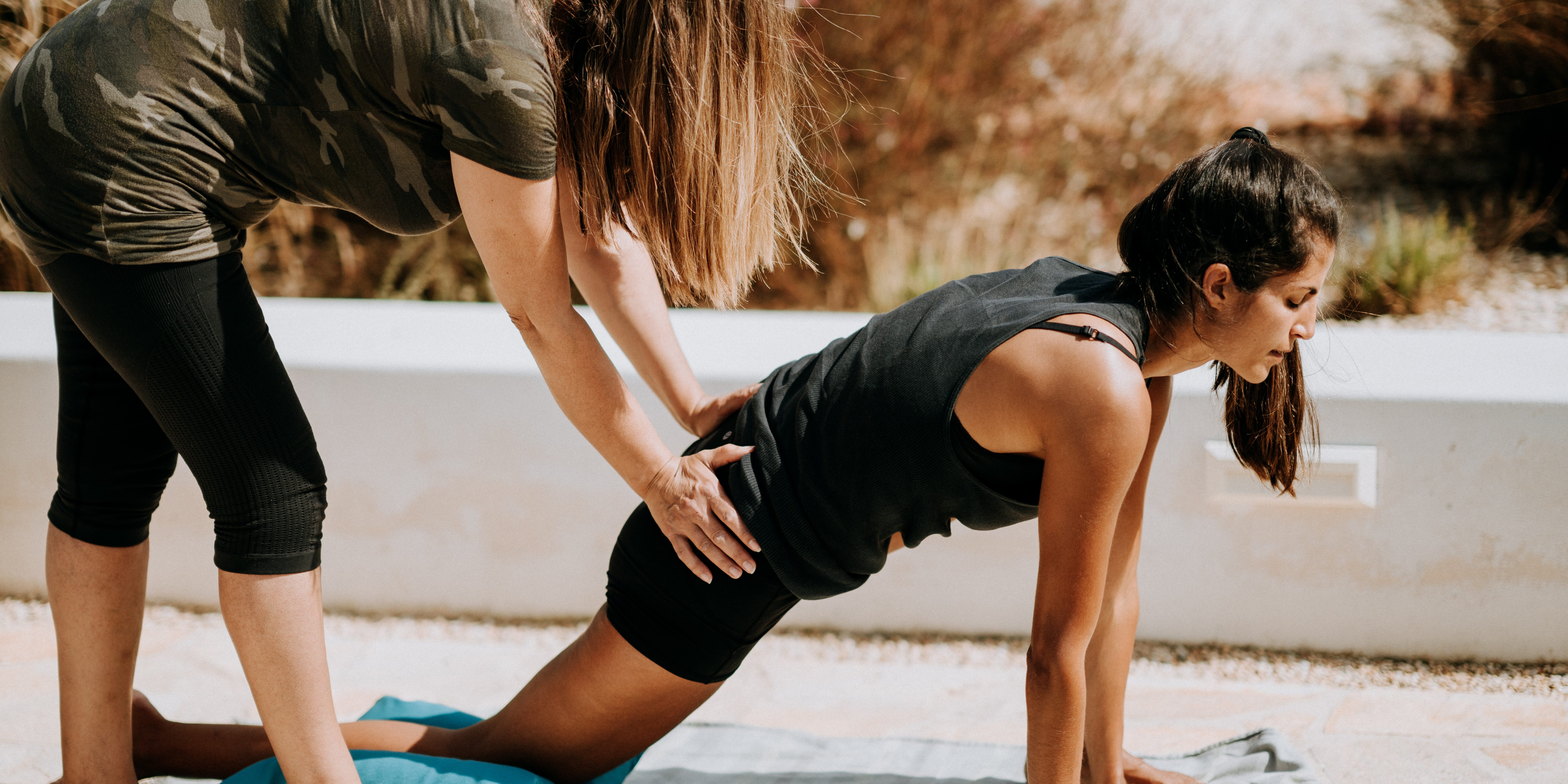
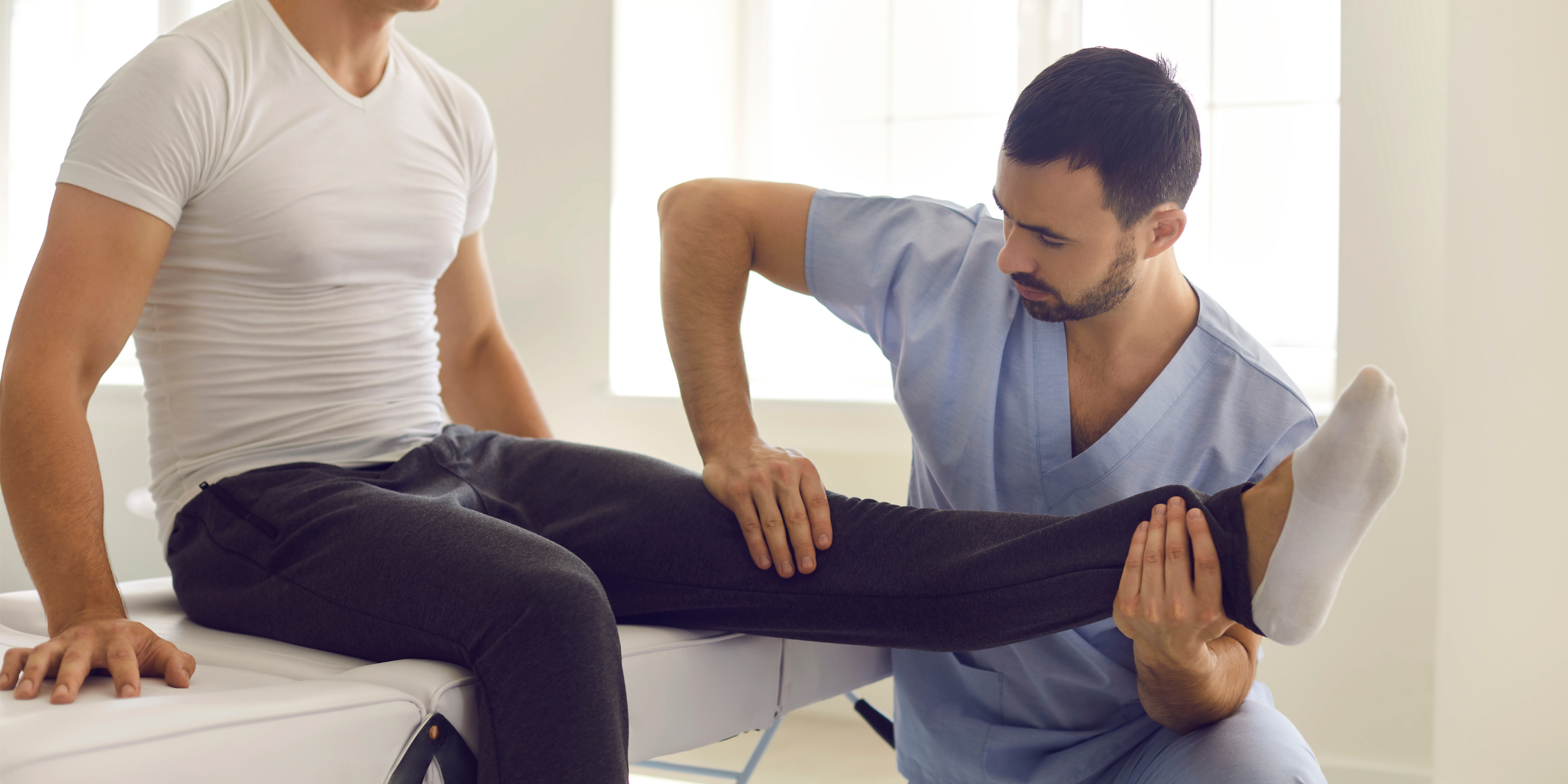
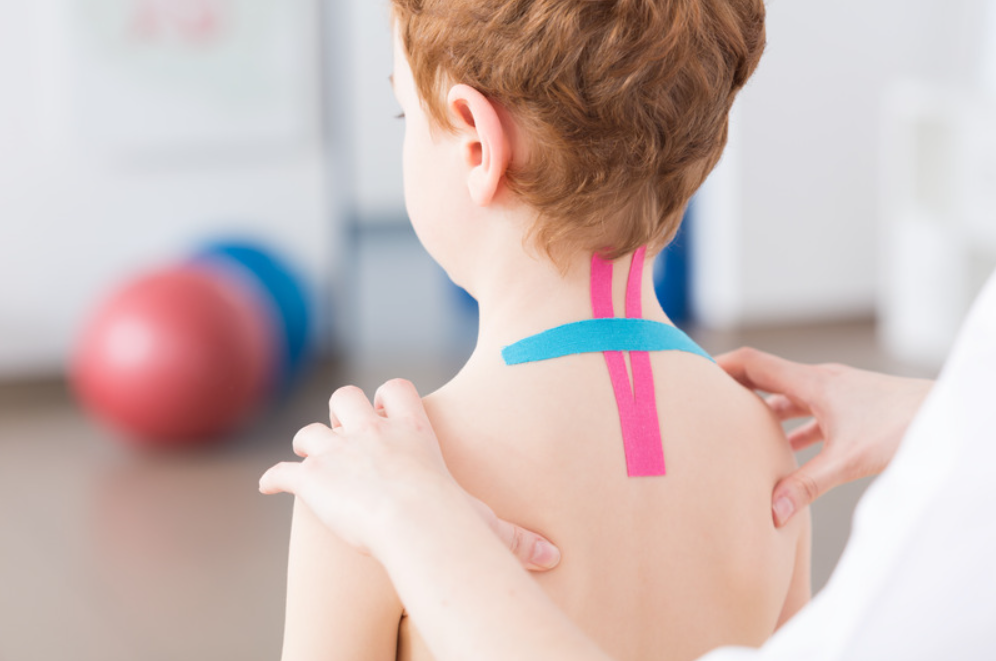
Physiotherapy involves a range of interventions aimed at improving physical function, mobility, and overall well-being. PT utilizes exercises, massages, and treatments based on physical stimuli such as heat, cold, electrical currents, or ultrasound. The primary goal is to relieve pain, enhance movement, and strengthen weakened muscles. PT practitioners also assess a patient’s condition, previous level of function, and how their present condition impacts daily life. Benefits of PT include pain management, improved mobility, and muscle strengthening, making it invaluable for individuals healing from injuries, disabilities, or health conditions.
What is Occupational Therapy?
Occupational Therapy focuses on helping individuals of all ages with physical, sensory, or cognitive challenges regain independence in various aspects of life. OT interventions address barriers affecting emotional, social, and physical needs. This may involve daily activities such as bathing, dressing, and eating, recommending adaptive equipment and providing caregiver and family training. OT aims to help patients develop, recover, and maintain the skills needed to perform daily activities, promoting autonomy and overall well-being.
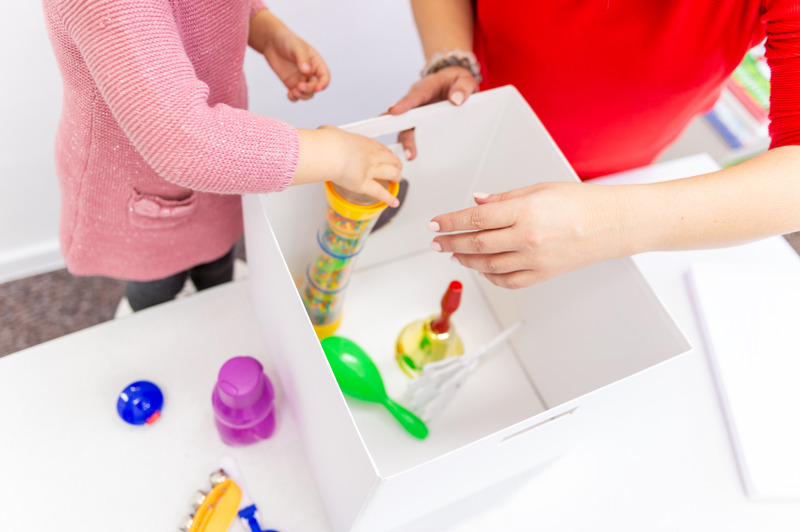

What is Pediatric Physiotherapy?
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in pediatric care, offering tailored interventions to address a wide range of physical challenges faced by children with diverse needs. From infants to adolescents, physiotherapists utilize specialized techniques and exercises to improve mobility, strength, and overall physical function. For children with developmental delays, neurological conditions, or musculoskeletal issues, physiotherapy provides invaluable support in achieving developmental milestones, enhancing motor skills, and promoting independence.
Whether it’s helping a child with Cerebral Palsy improve their balance and coordination or assisting a child with Down Syndrome in mastering activities of daily living, physiotherapy empowers children to overcome obstacles and thrive in their physical abilities. With a patient-centered approach and a focus on holistic care, physiotherapists collaborate closely with families and other healthcare professionals to ensure that each child receives the personalized support they need to reach their full potential.
What is Pediatric Occupational Therapy?
Occupational Therapy is a vital component of pediatric care, offering specialized interventions to address the unique challenges faced by children with diverse needs. Occupational therapists work closely with children and their families to promote independence in activities of daily living, enhance sensory processing, and improve fine motor skills. For children with developmental disorders, sensory processing difficulties, or physical disabilities, occupational therapy provides tailored strategies to overcome barriers and participate fully in meaningful activities.
Whether it’s helping a child with Autism Spectrum Disorder develop social skills and self-care routines or supporting a child with Sensory Processing Disorder in regulating their responses to stimuli, occupational therapy empowers children to engage actively in their daily lives. With a focus on promoting functional independence and fostering a supportive environment, occupational therapists collaborate with families, educators, and other healthcare professionals to ensure that each child receives comprehensive care tailored to their unique strengths and needs.
Similarities and Differences
Similarities include:
- Both physical therapists and occupational therapists employ specialized assessments to diagnose conditions and develop tailored treatment plans.
- PT’s and OT’s are committed to addressing individuals’ holistic well-being, encompassing their mental, physical, emotional, and environmental aspects.
- Both professions utilize a variety of tools and equipment to facilitate therapeutic interventions effectively.
- PT’s and OT’s share a common goal of enhancing quality of life, with a particular focus on improving mobility and functional abilities, promoting independence, and fostering overall well-being.
Differences include:
- Physiotherapy primarily focuses on physical function, mobility, and muscle strength, utilizing exercises and modalities like heat and ultrasound, whereas OT addresses a broader range of needs including emotional, cognitive, and social aspects of daily living.
- Occupational therapy often involves environmental adaptations and recommendations for adaptive equipment to facilitate daily activities, while physical therapy may place more emphasis on therapeutic exercises and manual techniques.
- While physiotherapy typically targets specific physical impairments or injuries, OT interventions are more holistic, addressing the individual’s overall well-being and participation in meaningful activities.
- Physiotherapy primarily focuses on addressing gross motor skill development, whereas Occupational Therapy focuses on fine motor skill development.
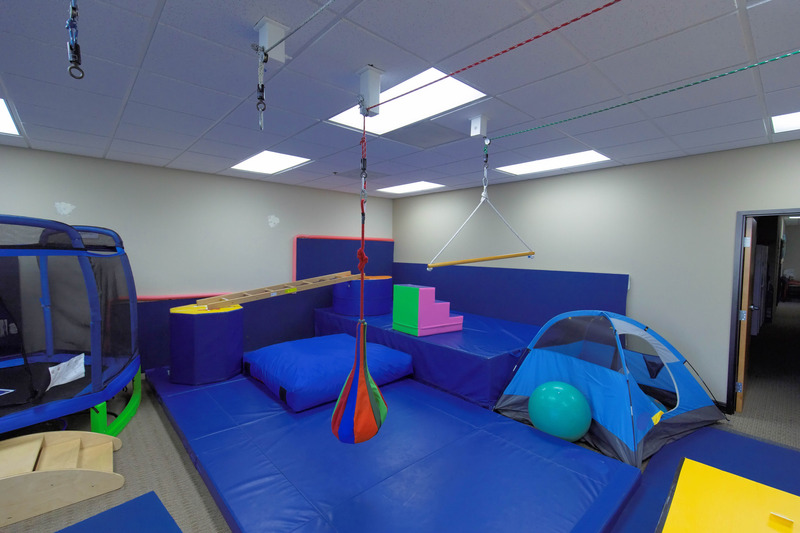

Pediatric physiotherapy and occupational therapy are indispensable components of comprehensive healthcare, particularly for children facing physical, sensory, or cognitive challenges. By working together, PT and OT professionals help children reach their full potential, enabling them to lead fulfilling and independent lives. Whether it’s improving mobility, enhancing daily living skills, or addressing emotional well-being, PT and OT play vital roles in supporting children’s growth and development.






