Introduction
Knee pain is a common complaint among athletes and fitness enthusiasts. Among the various knee injuries, one that often plagues individuals is Patellar Tendonitis, commonly known as Jumper’s Knee. This condition can be excruciating, hampering your ability to engage in physical activities, especially those that involve running and jumping. In this blog, we’ll delve into what patellar tendonitis is, how it affects you, and most importantly, how to prevent it and manage knee pain effectively through knee rehab.
What is Patellar Tendonitis?
Patellar tendonitis, often referred to as jumper’s knee, is an overuse injury characterized by pain in the tendon connecting your kneecap (patella) to your shinbone (tibia). It is typically caused by repetitive stress on the patellar tendon, which can occur in activities like running, jumping, and squatting. When the tendon is subjected to excessive strain, it can lead to tiny tears and inflammation, resulting in knee pain.
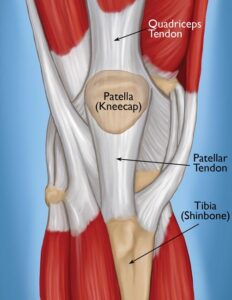
Anatomy of the Patellar Tendon
To understand patellar tendonitis better, it’s essential to know where the patellar tendon is located in the body and its purpose. The patellar tendon runs from the bottom of the patella to the top of the tibia and plays a crucial role in stabilizing the knee joint during activities that involve jumping, running, and quick changes in direction.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors can increase your susceptibility to patellar tendonitis. These include tight quadriceps, poor patellar tracking, improper foot, knee, or hip posture, and muscle imbalances. Engaging in activities or sports that involve running and jumping, such as basketball, volleyball, and soccer, also heightens the risk of developing this condition. Factors like the terrain or playing surface and sudden increases in physical activity levels can further contribute to the development of patellar tendonitis.
Signs and Symptoms
If you suspect you may have patellar tendonitis, watch out for these common signs and symptoms:
- Pain Location: You’ll typically experience pain just below the kneecap, often described as a dull, aching discomfort.
- Pain Triggers: Pain often occurs during activities that involve jumping, running, or bending the knee, and it may worsen with continued activity.
- Type of Pain: The pain can range from a mild annoyance to a severe, sharp pain that interferes with your daily activities.
Patellar Tendonitis in Children and Teens
Patellar tendonitis is not exclusive to adults; it’s also a common condition among children and teenagers. In this age group, it’s often associated with Osgood Schlatter and Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndromes. These conditions affect the patellar tendon’s insertion point on the tibia, leading to similar mechanisms of injury and signs and symptoms.
Preventing Knee Pain and Patellar Tendonitis
- Proper Warm-Up and Cool Down: Before starting any physical activity, it’s crucial to warm up your muscles and joints. A proper warm-up increases blood flow to the knee area, reducing the risk of injury. After your workout, cool down with gentle stretches to prevent muscle tightness.
- Gradual Progression: Avoid sudden increases in the intensity or duration of your workouts. Instead, gradually progress to more challenging activities to allow your body to adapt and strengthen over time.
- Strength Training: Building strong muscles around the knee can provide stability and support. Focus on exercises that target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles. A well-rounded strength training routine can reduce the strain on the patellar tendon.
- Proper Technique: Ensure you use proper form and technique during exercises and activities. This reduces unnecessary stress on your knee joints and tendons.
- Footwear: Invest in high-quality, well-fitting athletic shoes that provide adequate cushioning and support for your specific activity. Ill-fitting shoes can contribute to knee pain and injury.
Knee Rehab and Injury Management
If you do experience knee pain or suspect you have patellar tendonitis, it’s crucial to take action promptly. Here are some steps to manage knee pain effectively:
- Rest: Give your knee some time to heal by avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain. Rest is essential for recovery.
- Ice and Compression: Applying ice and using compression bandages can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Physical Therapy: Consult a physical therapist who can design a tailored rehabilitation program to strengthen your knee and improve flexibility.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs may help manage pain and swelling. Consult a healthcare professional before using any medication.
- Supportive Devices: Consider using knee braces or straps to provide extra support during physical activities.
- Patience and Persistence: Patellar tendonitis can be a stubborn injury to overcome. Be patient with your recovery process and follow your rehab plan diligently.
Exercises to Rehab/Prevent Jumper's Knee
Conclusion
Knee pain, especially due to patellar tendonitis or jumper’s knee, can be a significant setback for anyone pursuing an active lifestyle. However, by following proper injury prevention techniques, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition. If you do experience knee pain, early intervention, rest, and a comprehensive knee rehab plan are essential for a full recovery. Remember, your knee’s health is crucial to your overall well-being, so take good care of it to keep enjoying your favorite activities pain-free.





